Why Data Protection and Privacy Compliance is Critical for Modern Businesses
Data protection and privacy compliance has become one of the most complex challenges facing businesses today. With the global cost of data breaches reaching $4.45 million in 2023 and regulatory fines potentially reaching 4% of global revenue under GDPR, the stakes have never been higher.
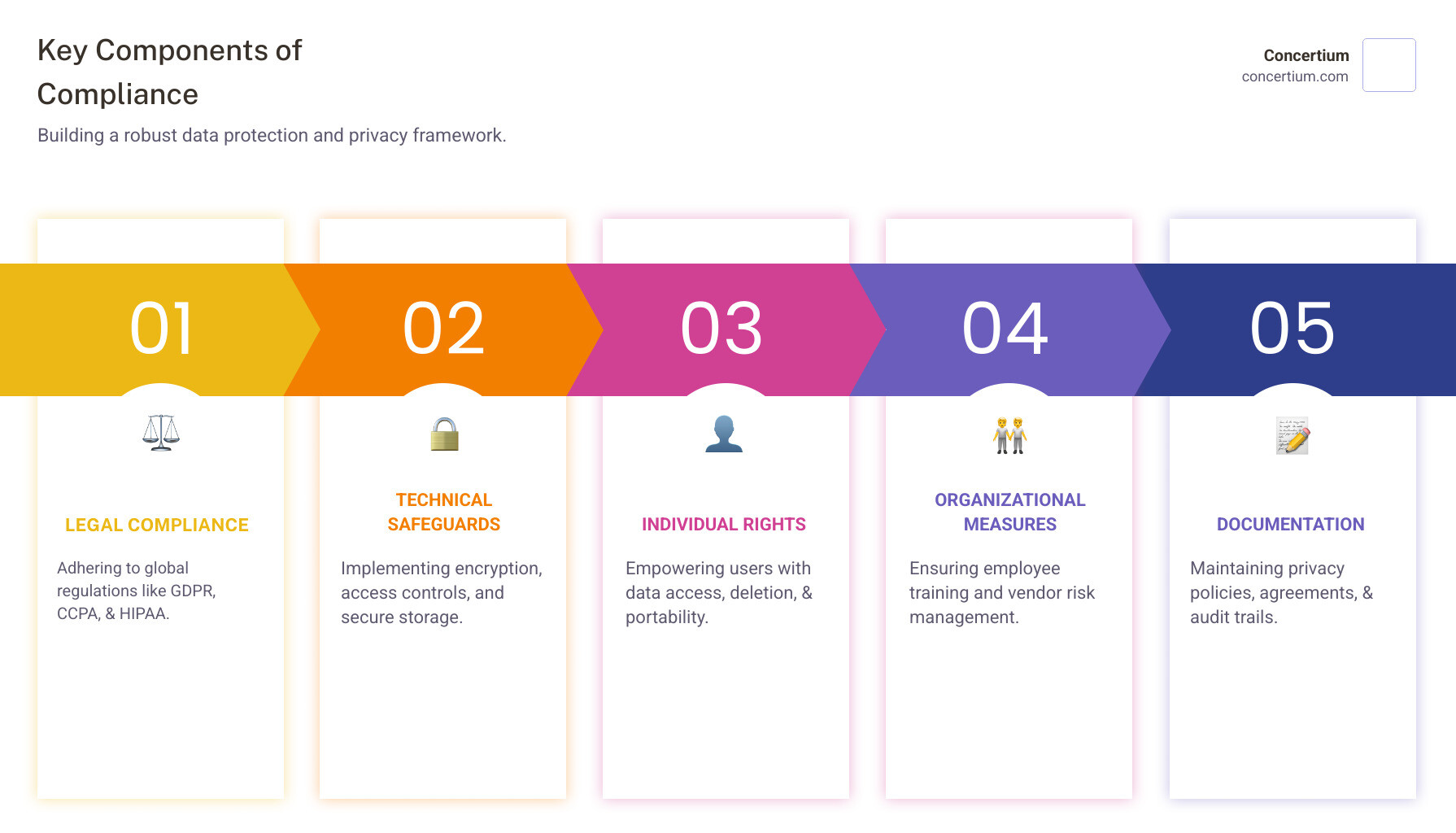
Key Components of Data Protection and Privacy Compliance:
- Legal Compliance: Following regulations like GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA
- Technical Safeguards: Encryption, access controls, and secure storage
- Individual Rights: Providing data access, deletion, and portability options
- Organizational Measures: Employee training and vendor management
- Documentation: Privacy policies, data processing agreements, and audit trails
The regulatory landscape continues to evolve rapidly. Fourteen US states currently have comprehensive data privacy laws in effect, with six more taking effect in 2025 and early 2026. Meanwhile, new laws are emerging globally in countries like India, Indonesia, Australia, and Saudi Arabia.
As one industry expert notes, “Running a business is complex, and there is no end to the number of different domains that you’ll need to be familiar with if you want to be successful.” Data privacy compliance represents one of these critical domains that can no longer be ignored.
The challenge isn’t just avoiding penalties. Organizations that invest in data privacy see a return of up to $2.70 for every dollar spent. Strong compliance builds customer trust, creates competitive advantages, and improves operational efficiency through better data governance.
Easy data protection and privacy compliance glossary:
- cybersecurity incident response planning
- enterprise security risk assessment
- cloud security risk management
Understanding the Foundations: Data Protection vs. Data Privacy
When we talk about data protection and privacy compliance, it’s easy to use the terms “data protection” and “data privacy” interchangeably. However, there’s a fundamental difference between the two, and understanding it is key to building a robust compliance strategy. Think of it like this: data privacy is the “what” and “why,” while data protection is the “how.”
Data privacy refers to the guidelines around how data should be collected, handled, and shared, based on its sensitivity and importance. It’s about ensuring that sensitive data is only accessible to approved parties and that individuals have control over their personal information. This includes defining who has the right to access data, how it’s used, and for what purposes. It’s fundamentally about an individual’s right to control their own information. For example, your personal health information (PHI) should only be accessible to your healthcare providers, and you should have the right to know how it’s being used.
On the other hand, data protection signifies the strategic and procedural steps we undertake to safeguard the privacy, availability, and integrity of sensitive data. Its goal is to prevent data corruption, loss, damage, or unauthorized access. Data protection provides the tools, technologies, and policies that actually restrict access to data. This involves all the technical and organizational measures we put in place, like encryption, access controls, and secure backups, to ensure that only authorized individuals can view and use data on a need-to-know basis.
A common misconception is that if you have one, you automatically have the other. Not quite! A company can be compliant with data protection standards without necessarily being truly private, and vice versa. For instance, a company might use robust security measures (data protection) but then share or sell your data without your informed consent (a privacy violation). Conversely, a company might have a great privacy policy, but if their systems are easily breached, they haven’t adequately protected your data.
Therefore, achieving true data protection and privacy compliance means addressing both aspects. We need clear privacy principles that dictate what we should do with data, combined with strong data protection mechanisms that ensure we can do it securely. It’s about building a system where the “who” and “why” are aligned with the “how” and “what.”
For a deeper dive into the security aspect, check out our guide on What is Data Security Compliance?
The Global Regulatory Landscape: Key Laws and Principles
Navigating data protection and privacy compliance means understanding a complex web of regulations. While the landscape is vast, a few key laws and their shared principles form the foundation.
The European Heavyweight: GDPR
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is the EU’s gold standard for data privacy. It applies globally to any business processing the personal data of EU residents. Fines for non-compliance are severe, reaching up to €20 million or 4% of global annual revenue.
For cybersecurity professionals, understanding GDPR Compliance in Cybersecurity isn’t optional – it’s essential.
California Leading the Way: CCPA and CPRA
In the US, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and its successor, the California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA), lead the way. These laws grant California residents significant rights, including the ability to access, delete, and opt out of the sale or sharing of their personal data. Fines range from $2,500 to $7,500 per violation.
Healthcare’s Special Rules: HIPAA
For organizations handling health information in the US, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is paramount. It mandates strict protection for patient health information (PHI) across healthcare providers and their partners. Violations can lead to significant financial and criminal penalties. Our guide on HIPAA Breach Prevention Best Practices can help you stay on the right side of these requirements.
The Growing Global Movement
The trend is global. In the United States, fourteen states currently have comprehensive privacy laws, with more on the way. Countries like India, Australia, and Brazil are also implementing their own frameworks. This creates challenges for international data transfers, often requiring specific legal mechanisms like the EU/UK/Swiss-US Data Privacy Framework to ensure data flows legally across borders.
Here’s how the major frameworks stack up:
| Feature | GDPR | CCPA/CPRA |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | EU/EEA residents, globally | California residents, primarily |
| Core Principle | Lawfulness, fairness, transparency | Consumer rights over personal info |
| Consent | Explicit (opt-in) for most processing | Opt-out for sale/sharing |
| Data Subject Rights | Access, rectification, erasure, portability | Access, delete, opt-out, correct, limit use |
| Breach Notification | 72 hours to DPA | “Without undue delay” to affected individuals |
| Penalties | Up to €20M or 4% of global revenue | $2.5K-$7.5K per violation |
Core Principles Guiding Global Privacy Laws
Despite their differences, most privacy laws share a common foundation. These core principles are your North Star for data protection and privacy compliance.
- Lawfulness, fairness, and transparency: Be upfront about what data you collect, why, and how you use it.
- Purpose limitation: Only use data for the specific purpose for which it was collected.
- Data minimization: Collect only the data that is absolutely necessary.
- Accuracy: Ensure the data you hold is accurate and up-to-date.
- Storage limitation: Don’t keep data longer than necessary. Securely delete it once its purpose is fulfilled.
- Integrity and confidentiality: Protect data from unauthorized access or attack through robust security measures.
- Accountability: Be able to demonstrate your compliance with these principles through documentation and clear policies.
Following these principles helps you meet regulatory requirements while building genuine trust with your customers. For a deeper dive into how these principles connect with broader security frameworks, explore our guide on Cybersecurity Compliance Standards.
A Practical Blueprint for Data Protection and Privacy Compliance
Building effective data protection and privacy compliance is a systematic process. This practical blueprint breaks it down into four manageable steps.
Step 1: Data Findy, Inventory, and Classification
You can’t protect what you don’t know you have. The first step is to find, inventory, and classify all personal data your organization holds. This includes Personally Identifiable Information (PII), Protected Health Information (PHI), and other sensitive data.
Data mapping is essential to understand the entire data lifecycle: where it comes from, how it moves, who accesses it, and where it’s stored. Use automated findy tools to scan your infrastructure and classify data based on sensitivity and regulatory rules. This process naturally supports data minimization, helping you identify and eliminate unnecessary data, which reduces risk and simplifies compliance.
For organizations looking to strengthen their overall governance approach, our guide on IT Governance, Risk and Compliance provides valuable insights into building comprehensive data management strategies.
Step 2: Implement Key Technologies for Data Protection and Privacy Compliance
Once you know what data you have, implement key technologies to protect it.
- Encryption is fundamental for data at rest and in transit, making it unreadable to unauthorized parties.
- Access controls are critical. Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) to secure logins and use Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) to ensure employees can only access data relevant to their jobs.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP) solutions monitor and block risky data movements to prevent leaks.
- Secure backups and disaster recovery procedures are vital. Follow the 3-2-1 backup rule (three copies, two media types, one off-site) and consider immutable storage to protect backups from ransomware.
For organizations wanting to dive deeper into preventing data loss, our comprehensive guide on Data Loss Prevention Compliance offers detailed strategies and best practices.
Step 3: Ensure Transparency and Uphold User Rights
Technology isn’t enough; transparency builds trust. Your privacy policy must be clear and easy to understand, explaining what data you collect, why, how you use it, and your retention periods.
Implement robust consent management with granular, easy-to-use options for users to give or withdraw consent. Be prepared to handle Data Subject Access Requests (DSARs) efficiently. This includes fulfilling the right to access, rectification, erasure (or “right to be forgotten”), data portability, and the right to opt-out of data sales or sharing. Automating these processes is key to respecting user rights promptly.
For organizations building comprehensive risk management strategies, our resource on Compliance and Risk Management provides broader context for integrating privacy rights into overall business operations.
Step 4: Build a Culture of Continuous Data Protection and Privacy Compliance
Compliance is an ongoing culture, not a one-time project. Make privacy everyone’s responsibility through continuous effort.
- Employee training is essential to empower your workforce to handle data responsibly.
- Vendor management and third-party risk assessments are critical. Use Data Processing Agreements (DPAs) to set clear expectations with partners.
- Privacy Impact Assessments (PIAs) help you proactively identify risks before launching new products or systems.
- Regular audits, both internal and external, maintain your program’s effectiveness.
This creates a continuous cycle of assessment and improvement, ensuring your compliance program evolves with your business and the changing regulatory landscape. For practical guidance on conducting thorough compliance evaluations, our article on Compliance Risk Assessment offers expert insights and actionable strategies.
Navigating Modern Challenges and Future Trends
The world of data protection and privacy compliance is never static. New technologies and evolving threats demand constant adaptation.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) presents a major privacy challenge. Large Language Models (LLMs) require vast amounts of training data, creating risks if sensitive information is included. Organizations must implement strict governance over AI training data, use data sanitization techniques, and control access to AI systems. Integrating data protection principles into AI governance is quickly becoming a regulatory necessity.
Ransomware and cybersecurity threats are evolving. Attackers now often steal data before encrypting it, creating a double extortion threat. This makes robust defenses and recovery plans more critical than ever. Immutable storage for backups is a key defense, as it prevents ransomware from altering or deleting backup data. Continuous strengthening of network security, endpoint protection, and intrusion detection is essential for maintaining compliance.
Data portability is an emerging right, allowing individuals to move their data between services. This requires businesses to design systems that facilitate secure data transfers while respecting data sovereignty—the laws of the location where data is stored.
The move to cloud services introduces the shared responsibility model. Cloud providers (e.g., AWS, Azure) secure the cloud infrastructure itself, but you are responsible for securing what’s in the cloud: your data, applications, and configurations. Using a compliant provider does not automatically make your business compliant; you must still manage access controls, encryption, and user permissions correctly.
These trends show that data protection and privacy compliance requires constant vigilance. Proactive risk management and continuous monitoring are not optional. Staying ahead of these changes builds customer trust and creates a significant competitive advantage. For more insights on how we help organizations steer these complex challenges, explore our approach to Cybersecurity Risk Management.
Frequently Asked Questions about Data Protection and Compliance
Here are answers to common questions about data protection and privacy compliance.
What is the difference between data protection and data privacy?
Data privacy is about the rules and rights governing personal information: who can access it, how it’s used, and what control individuals have. It’s the ‘why’ and ‘what’.
Data protection refers to the technical and organizational safeguards used to secure that data, such as encryption and access controls. It’s the ‘how’. You need both for comprehensive compliance.
Does using a compliant cloud provider like AWS or Azure make my business compliant?
No. Using a compliant cloud provider like AWS or Azure does not automatically make your business compliant. Cloud security operates on a shared responsibility model. The provider is responsible for the security of the cloud (the infrastructure), but you are responsible for security in the cloud. This includes securing your data, managing access controls, configuring applications correctly, and meeting all regulatory requirements for how you use the service. The ultimate compliance responsibility is yours.
What are the potential penalties for non-compliance with laws like GDPR?
Penalties for non-compliance are severe and multi-faceted. They include:
- Heavy Financial Fines: GDPR fines can reach up to €20 million or 4% of global annual revenue. CCPA fines range from $2,500 to $7,500 per violation. These can quickly escalate into millions for large-scale breaches.
- Reputational Damage: Losing customer trust is often more damaging than the financial penalty. Privacy-conscious consumers will take their business elsewhere, and rebuilding a tarnished reputation is a long, expensive process.
- Legal Action and Business Disruption: Non-compliance can lead to lawsuits from individuals and consumer groups. Regulatory investigations can also disrupt operations and even block access to key markets.
The cost of non-compliance far outweighs the investment in a robust compliance program.
Conclusion
Navigating the intricate maze of data protection and privacy compliance is more than just checking boxes to avoid fines. It’s about building a foundation of trust that can transform your business.
Compliance is truly a journey, not a destination. The regulatory landscape keeps evolving, new technologies emerge, and cyber threats become more sophisticated. Organizations that accept this challenge gain a significant advantage.
We’ve walked through the key distinctions between data protection (the “how”) and data privacy (the “why”), explored the global regulatory landscape, and laid out a practical blueprint that turns compliance from a burden into a business asset.
Building trust through strong compliance practices creates incredible value. When customers know their data is safe, they are more likely to engage with your services. That trust translates into real business outcomes: stronger customer relationships, reduced churn, and competitive advantage.
The numbers back this up. Organizations investing in data privacy see returns of up to $2.70 for every dollar spent. This isn’t just about avoiding hefty fines; it’s about gaining operational efficiency and the kind of customer loyalty earned through responsible data practices.
The ROI of privacy extends far beyond compliance costs. Better data governance leads to cleaner databases and faster business insights. Strong security reduces breach risks and their associated costs. Clear privacy policies build a brand reputation that pays dividends for years.
At Concertium, we’ve been helping organizations steer these challenges for nearly 30 years. We understand that every business is different, which is why our Collective Coverage Suite (3CS) provides custom solutions with AI-improved observability and automated threat eradication. We build sustainable, compliant operations that grow with your business.
Your data protection and privacy compliance journey doesn’t have to be a solo trip. We’re here to help you build a program that protects your customers, satisfies regulators, and drives real business value.
Ready to turn compliance into competitive advantage?