Penetration testing — often called ethical hacking — is a controlled simulation of attacker behavior that surfaces exploitable weaknesses before they become incidents. This guide shows how pentests reveal gaps across web apps, networks, cloud, and people processes, and how organizations can prioritize fixes to lower breach risk and meet regulatory obligations.
You’ll learn what a pentest includes, which test types match which risks, how a disciplined methodology delivers actionable findings, and how testing maps to frameworks like PCI DSS, SOC 2, HIPAA, and ISO 27001. We balance technical clarity with business priorities — risk reduction, incident readiness, and audit evidence — so security, engineering, and leadership teams can make informed choices. We also describe modern approaches, such as AI-enhanced observability and vulnerability risk management, and finish with FAQs and next steps to scope a test that fits your risk profile.
What Are Penetration Testing Services and Why Do They Matter?
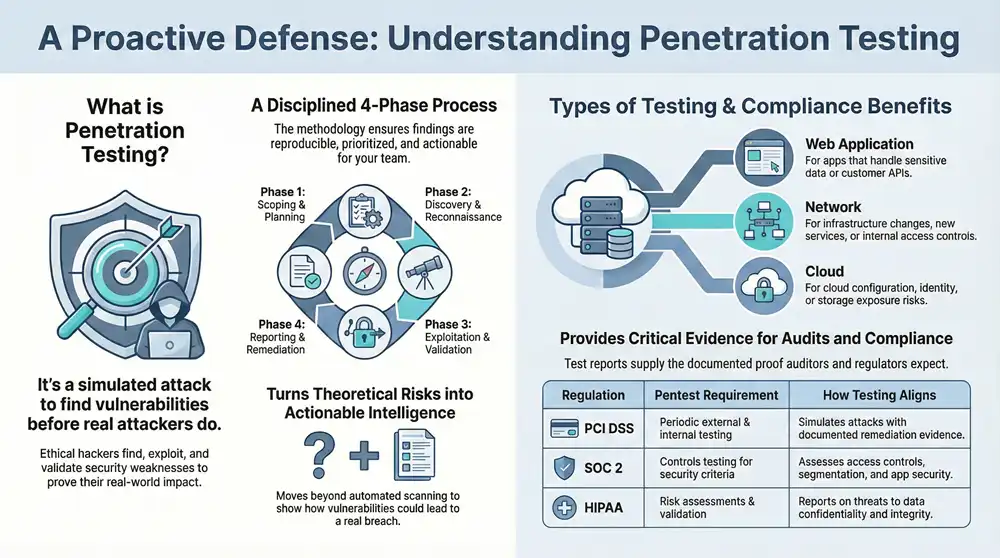
Penetration testing is a structured security assessment where ethical hackers simulate targeted attacks to find, exploit, and validate vulnerabilities so you can fix them before real attackers do. Tests combine automated scans with hands-on techniques — reconnaissance, exploitation, and controlled post‑exploit steps — to prove impact and produce prioritized remediation guidance. Pen tests turn theoretical risk into demonstrable exploitability, reduce the chance of breaches, and yield the evidence auditors and regulators expect. Regular testing shrinks the attack surface, strengthens incident response, and feeds continuous security improvement. Knowing how penetration testing complements vulnerability scanning helps teams prioritize real risk rather than chasing noisy scan output.
How Does Penetration Testing Find Security Vulnerabilities?
Penetration testing follows a clear sequence: targeted reconnaissance to map assets and entry points; automated scanning to flag known issues; and manual exploitation to validate impact and chain vulnerabilities into realistic attack paths. Testers create proof‑of‑concept exploits and perform controlled post‑exploitation steps to show how an attacker could escalate privileges, exfiltrate data, or disrupt services — always within agreed rules of engagement. Findings are validated, de‑duplicated, and risk‑scored so teams receive prioritized, actionable remediation instead of raw scan lists. Follow‑up validation confirms fixes and maintains confidence in your controls.
What Business Value Comes from Regular Penetration Testing?
Regular pentesting delivers measurable value beyond technical fixes: it lowers breach likelihood, supports audits, and reassures stakeholders with objective security validation. Frequent testing guides patching and configuration priorities, shortens exposure windows for high‑risk issues, and reveals gaps in detection and response. Pen tests also provide the technical evidence auditors need, helping you meet contractual and regulatory requirements. Together, these outcomes reduce cyber risk, make security spending more effective, and boost resilience to targeted attacks.
Which Types of Penetration Testing Does Concertium Offer?
Penetration testing spans several focused types — web application, network, cloud, API, mobile, social engineering, and red team simulations — each targeting a different attack surface and producing distinct outputs. The right test depends on asset exposure, compliance needs, and potential business impact. For example, web app testing centers on OWASP Top 10 issues and APIs, while network tests examine perimeter controls and internal segmentation. Concertium’s offerings, like Deep Network Assessment and Vulnerability Risk Management, map directly to these needs, supporting both point-in-time assessments and continuous remediation programs. Below is a practical comparison to help you choose the right approach for your risk profile.
Different penetration test types, scopes, and typical deliverables:
When to choose each test type:
- Web application testing: If applications handle sensitive data or expose customer/partner APIs.
- Network testing: If infrastructure changes, new services, or internal access controls are in question.
- Cloud testing: If cloud configuration, identity, or storage exposure could enable compromise.
These guidelines steer teams toward the test that best matches immediate security and compliance goals.
What Is Web Application Penetration Testing and Why It Matters
Web application pentests focus on application logic, input validation, authentication, authorization, and API security — common sources of OWASP Top 10 flaws. Testers try to exploit issues like injection, broken access control, and insecure deserialization to show real impact on data confidentiality and integrity. Deliverables typically include a prioritized vulnerability list, reproduction steps, and developer‑focused remediation guidance tied to secure coding practices. Since modern apps rely on microservices and exposed APIs, effective web pentests also examine API schemas and authentication flows to map attacker paths end to end.
How Does Network Penetration Testing Protect Internal and External Systems?
Network testing assesses perimeter defenses as well as internal trust relationships, wireless infrastructure, and IoT to find opportunities for lateral movement and privilege escalation. External tests target internet‑facing services and misconfigurations; internal tests simulate an attacker who already has a foothold and attempts to pivot to sensitive assets. Findings typically lead to improved network segmentation, prioritized patching, access control changes, and firewall or VLAN policy updates. Those changes reduce the chance that a single compromise causes widespread disruption.
How Does Concertium’s Penetration Testing Methodology Deliver Thorough Evaluation?
Our methodology blends planning, reconnaissance, testing, exploitation, reporting, and remediation support so findings are reproducible, prioritized, and actionable. We align scopes and risk scoring to standards such as OWASP and NIST, and our manual testing uncovers logic flaws that automated tools miss. AI‑enhanced observability adds value by correlating telemetry, surfacing anomalies, and expanding scope discovery, which improves coverage and context. This hybrid model produces evidence‑rich reports engineering teams can act on quickly, and it supports retesting to confirm remediation.
Phases of a comprehensive pentest, with expected activities and deliverables:
We integrate AI‑Enhanced Advanced Observability into several phases to refine scope and risk prioritization. Logs, traces, and metrics help testers validate exploit impact and correlate vulnerabilities with real telemetry, reducing false positives. After testing, our managed services and Vulnerability Risk Management programs track remediation until issues are closed, turning findings into sustained risk reduction.
What Are the Phases of Concertium’s Penetration Testing Process?
Our process typically follows a 4–6 phase model, starting with scoping and ending with remediation validation. Scoping sets asset boundaries and compliance targets. Reconnaissance builds an attack surface map using discovery tools and observability telemetry. Exploitation demonstrates business impact with proof‑of‑concept exploits and chained attack paths. Reporting prioritizes fixes by risk and operational impact. Finally, remediation support and verification confirm fixes and fold findings into long‑term vulnerability workflows. The result is a repeatable cycle that drives continuous security improvement.
How Is AI-Enhanced Observability Used in Penetration Testing?
AI‑enhanced observability helps by correlating logs, traces, and metrics to exposed vulnerabilities and suggesting likely attack paths based on historical telemetry. Machine assistance speeds scope discovery, highlights anomalous service behavior, and helps rank findings by real‑world impact. Human experts validate and contextualize those results to avoid over‑reliance on automation. Observability also makes exploit impact clearer in reports, enabling smarter remediation prioritization and faster time‑to‑fix. The human‑in‑the‑loop approach combines machine speed with expert judgment for higher‑confidence outcomes.
How Does Penetration Testing Support Compliance with Industry Regulations?
Penetration testing provides tangible evidence that security controls work and helps meet regulatory expectations for testing and risk assessment. Many standards require periodic tests, proof of remediation, and documented risk processes; pentests supply the artifacts auditors expect: scoped plans, test reports, and remediation evidence. Mapping tests to compliance frameworks ensures findings are presented in auditor‑friendly terms and that recommendations address specific control objectives. Below is a concise mapping showing how penetration testing aligns with major regulations.
Compliance mapping: regulation → pentest requirement → how testing meets it
Penetration testing both satisfies explicit testing mandates and strengthens your control environment so auditors can verify remediation and effectiveness. Test results become part of the documentation package that demonstrates due diligence and ongoing monitoring.
Which Compliance Standards Require Penetration Testing?
A number of common frameworks either require or strongly recommend penetration testing. PCI DSS explicitly mandates periodic pentests for cardholder environments. SOC 2 expects organizations to validate that security controls operate effectively — testing helps demonstrate that. HIPAA calls for risk analysis and mitigation, where targeted pentests provide validating evidence. ISO 27001 and NIST guidance also recommend regular testing as part of an effective information security management system. Knowing each standard’s expectations helps you plan the right scope and cadence for audits.
How Does Concertium Align Testing with PCI DSS, HIPAA, SOC 2, and ISO 27001?
We align penetration testing deliverables to compliance goals by mapping findings to control objectives and producing auditor‑ready evidence: scoped plans, technical findings with remediation verification, and post‑test validation summaries. For PCI DSS we focus on cardholder environments; for HIPAA we emphasize safeguards for protected health information; SOC 2 and ISO 27001 mappings tie findings to control criteria and risk treatment plans. That alignment supports audit workflows and helps you show remediation and continuous improvement in a clear, traceable way.
Why Choose Concertium for Expert Penetration Testing Services?
Choosing a pentest provider requires more than technical skill. You gain the most when testing is integrated into wider risk management and remediation programs. Concertium combines technical assessments with programmatic follow‑through — linking pentests to vulnerability risk management and managed security services to cut time‑to‑remediate. Our AI‑Enhanced Advanced Observability and Post‑Breach Services mean testing not only finds issues but also helps validate detection and response readiness. Below are the core ways we help enterprises meet their security objectives.
Concertium’s distinct value propositions:
- End-to-end security lifecycle support: Testing tied to remediation tracking and vulnerability risk management.
- AI-enhanced observability: Telemetry‑driven scope discovery and impact validation.
- Managed cybersecurity services: Ongoing operational support to reduce residual risk.
- Post-breach services and compliance advisory: Incident readiness and audit‑aligned reporting.
What Unique Value Propositions Does Concertium Provide?
Our solutions mix program-level services and technical offerings so you close the loop from discovery to resolution. The Collective Coverage Suite (3CS) and Managed Cybersecurity Services provide continuous oversight, while Deep Network Assessment and Vulnerability Risk Management deliver focused testing and remediation workflows. AI‑Enhanced Advanced Observability improves evidence collection and prioritization, and Post‑Breach Services support containment and recovery when needed. Together, these capabilities help you find vulnerabilities and reliably track and verify fixes within a broader security program.
How Do Case Studies Show Concertium’s Penetration Testing Results?
Strong case studies follow a challenge → approach → outcome format and highlight measurable improvements like reduced attack surface, fewer critical findings, or faster remediation. An anonymized example could describe a client with an exposed API (challenge), a coordinated web app and API pentest with observability correlation (approach), and a 70% reduction in high‑risk findings plus verified remediation (outcome). Case blurbs focus on scope, quantifiable results, and the testing‑to‑remediation lifecycle so prospective clients can judge relevance while preserving confidentiality.
What Are Common Questions About Penetration Testing Services?
This section answers practical questions security teams and decision‑makers ask when planning penetration tests, offering concise guidance on frequency, scope, and cost factors. Clear answers set realistic expectations and help you choose a delivery model — one‑off assessment, scheduled testing, or continuous PTaaS-style programs — that matches your risk profile and compliance needs. Short answers are followed by brief explanations to support scoping conversations.
Common planning considerations in list form:
- Testing frequency: Baseline cadence and triggers for extra testing.
- Scope definition: Asset selection, criticality, and compliance mapping.
- Delivery models: One‑off engagements, scheduled retests, and managed programs.
How Often Should Companies Perform Penetration Testing?
At minimum, perform penetration testing annually and after significant changes to infrastructure, applications, or processes that affect exposure. High‑risk systems, customer‑facing apps, and regulated environments often need more frequent checks — quarterly or after major releases — to keep protections current. Continuous monitoring and vulnerability risk management complement periodic tests by addressing fast‑moving threats and shortening remediation cycles. Set cadence based on risk and compliance requirements so tests stay relevant and effective.
What Is the Average Cost and Scope of Penetration Testing Services?
Costs vary by scope, complexity, and delivery model. Rather than fixed prices, think in effort bands: small scoped web app tests, medium multi‑application or network assessments, and large red team simulations that exercise detection and response. Key cost drivers include asset count, application complexity, compliance evidence needs, and whether observability integration or remediation support is included. Request a scoping conversation to define assets, desired depth, and deliverables — that produces a tailored quote and aligned expectations on timeline and outcomes.
To schedule a tailored assessment or technical scoping call, request a consultation to define scope, deliverables, and remediation integration with your vulnerability management program. Concertium services — Deep Network Assessment, Vulnerability Risk Management, AI‑Enhanced Advanced Observability, Managed Cybersecurity Services, and Post‑Breach Services — can combine into a program that matches your risk tolerance and compliance needs. Early scoping ensures tests focus on your highest‑risk assets and produce audit‑ready evidence.
- Scoping clarity: Define assets and compliance requirements first.
- Delivery alignment: Choose a one‑off test or ongoing program based on risk.
- Outcomes focus: Prioritize remediation and verification to close findings efficiently.
Frequently Asked Questions
What qualifications should I look for in a penetration testing provider?
Look for hands‑on certifications such as Offensive Security Certified Professional (OSCP) or Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH), and leadership credentials like CISSP where relevant. Industry experience and familiarity with your compliance landscape (PCI DSS, HIPAA, etc.) matter. Ask about methodologies, tooling, and anonymized case studies to verify practical results. A provider that integrates findings into a broader security program and emphasizes continuous improvement is ideal.
How can penetration testing improve my organization's incident response?
Penetration testing improves incident response by revealing likely attack vectors and weaknesses before they’re exploited. Tests help teams validate detection coverage, refine playbooks, and train responders on realistic scenarios. Findings inform detection tuning and response rehearsals, shortening reaction times and reducing impact during real incidents.
What is the difference between penetration testing and vulnerability scanning?
Vulnerability scanning is an automated sweep that lists known issues. Penetration testing goes further: skilled testers exploit vulnerabilities to show real impact and chain weaknesses into practical attack paths. Scanning is a useful baseline; pentesting provides deeper, prioritized insight and actionable remediation advice.
How do I prepare my organization for a penetration test?
Prepare by clearly defining scope, getting stakeholder buy‑in, and arranging necessary permissions. Hold a pre‑test meeting to set objectives, rules of engagement, and communications channels. Provide relevant documentation — network diagrams, architecture notes, and security policies — and ensure your incident response team knows how you’ll handle findings or test impact during the engagement.
What should I expect in the final report after a penetration test?
Your final report should include an executive summary, detailed technical findings, prioritized remediation recommendations, and evidence such as screenshots or logs. The executive summary frames risk for leadership; the technical section provides reproducible steps and developer‑focused fixes. Good reports also recommend retesting and integration points for vulnerability management.
Can penetration testing help with compliance requirements?
Yes. Many regulations — PCI DSS, HIPAA, SOC 2 — require or expect periodic testing. Penetration tests supply documented evidence of assessment and remediation that auditors look for. The reports and verification artifacts from testing help demonstrate due diligence and support compliance workflows.
Conclusion
Regular penetration testing is a practical way to discover and remediate vulnerabilities, reduce breach risk, and strengthen compliance posture. When testing is tied to ongoing risk management and remediation, organizations maintain a resilient security posture that adapts as threats evolve. Partnering with a provider like Concertium streamlines assessments and integrates findings into a program that matches your priorities. Ready to tighten your security posture? Reach out for a scoped consultation to get started.