Risk management cybersecurity is the ongoing process of identifying, assessing, and addressing digital threats to an organization’s information systems and data. It’s about understanding potential cyber dangers and taking smart steps to reduce their harm.
Here’s what it means in simple terms:
- Identify: Find out what digital assets you have and what risks they face.
- Assess: Figure out how likely a risk is to happen and how bad it would be.
- Address: Decide what to do about the risk – fix it, avoid it, share it (like with insurance), or accept it.
- Monitor: Keep checking your risks and defenses, because threats always change.
Organizations face diverse and clever threats, from cyberattacks to natural disasters, demanding an adaptive response. Managing cyber risks is increasingly complex due to cloud services, third-party vendors, new regulations, and the shift to remote work on less secure networks.
Cybercrime is a major, expensive threat. Healthcare data breaches can exceed $10 million on average, and with thousands of new vulnerabilities and malware variants emerging monthly, it’s a constant fight. A smart approach to risk management cybersecurity is essential for business continuity and building trust.
Risk management cybersecurity terms at a glance:
- Cybersecurity governance frameworks
- Cybersecurity compliance consulting
- Enterprise cybersecurity solutions
The Core Components of Risk Management Cybersecurity
At its heart, risk management cybersecurity isn’t just a technical issue; it’s a fundamental business risk. Cyber risk is the potential harm your business could face from a cybersecurity incident, from a data breach to a ransomware attack. It involves weighing the likelihood of an event against the potential impact on your operations.
Integrating Cybersecurity and Enterprise Risk Management (ERM)
At Concertium, we believe risk management cybersecurity must be deeply integrated into your organization’s broader Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) framework. ERM covers all potential risks to business goals, including financial, operational, and strategic. NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) agrees, stressing that risk management is the foundation of cybersecurity. Cybersecurity deserves significant attention within ERM programs, with ICT risk registers serving as vital inputs to the enterprise risk profile. This requires balancing an evolving threat landscape with business continuity.
Understanding Threats, Vulnerabilities, and Impact
To get a handle on cyber risk, we must break it down into its key ingredients.
Threats are potential events that could harm your systems or data. Examples include malware attacks, ransomware incidents (which caused an average of 21 days of downtime in 2023), social engineering like phishing, supply chain compromises, zero-day exploits, employee mistakes, and natural disasters.
Vulnerabilities are weaknesses a threat could exploit, like a misconfigured firewall, an unpatched software bug, or lax access controls. With about 2,000 new vulnerabilities added to the NIST National Vulnerability Database and thousands of new malware variants appearing monthly, staying vigilant is critical.
Finally, Impact is the harm caused if a threat exploits a vulnerability. Consequences include service disruption, downtime, lost revenue, stolen or destroyed sensitive data, damage to your reputation, and regulatory fines.
Common Cybersecurity Risks Your Organization Faces
Common cybersecurity risks are the real-world ways threats exploit vulnerabilities to impact your business.
Operational Risk is the danger of business activities halting, such as from a ransomware attack causing costly downtime. Financial Risk covers the direct and indirect costs of an incident. For example, data breaches cost the healthcare sector an average of USD 10.10 million and hospitality USD 2.9 million.
You also face Regulatory Risk from non-compliance with laws like GDPR and HIPAA, which can lead to massive fines. Third-Party Risk is significant, as the average company shares confidential data with 583 third parties, making supply chain attacks a growing concern. Finally, Reputational Risk from a cyber incident can damage your brand and erode customer trust, with recovery often being more costly than direct financial losses.
To steer these complexities, we often guide organizations to leverage Cybersecurity Compliance Standards as a solid foundation for their security posture. It’s all about building strong defenses from the ground up!
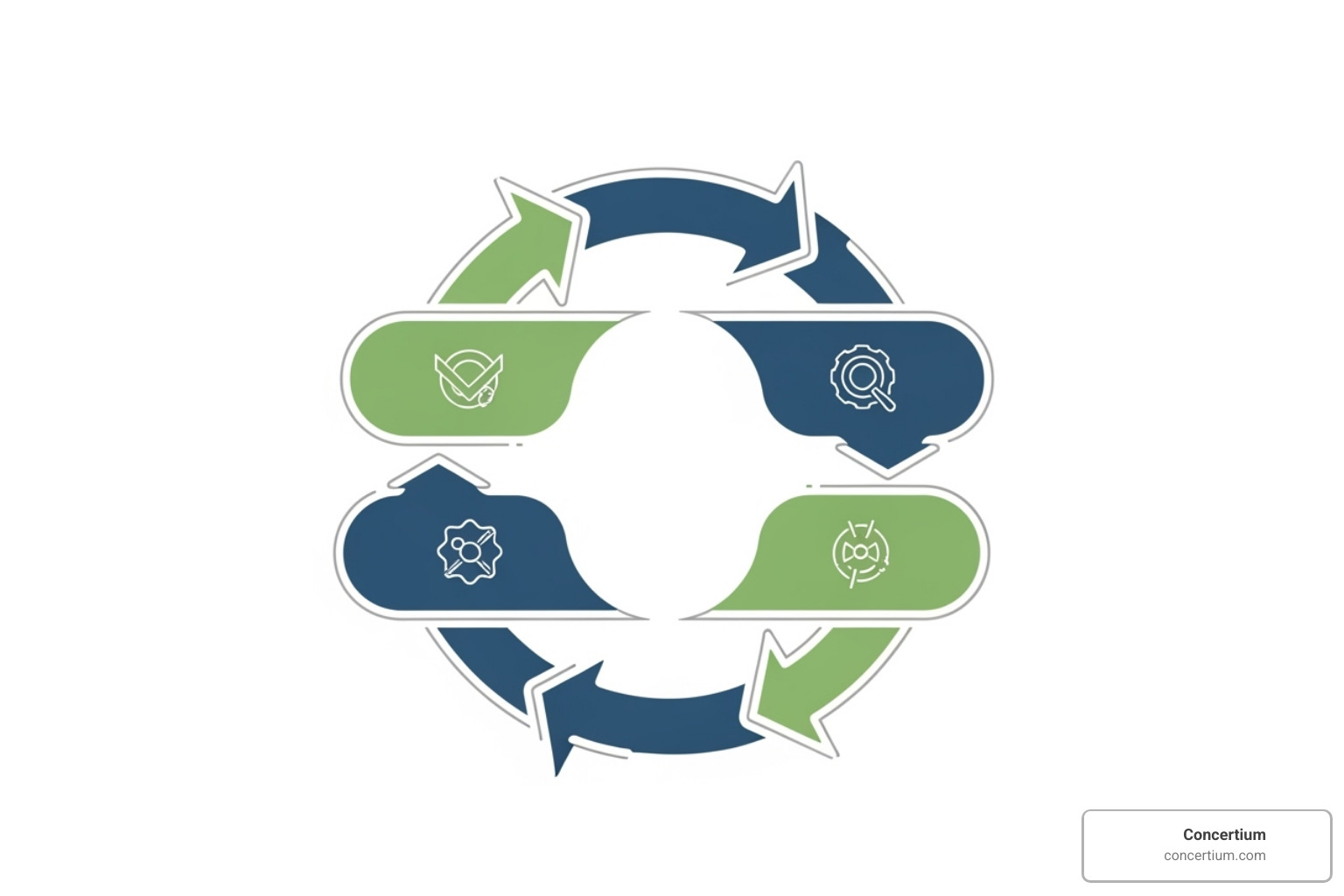
The Cybersecurity Risk Management Lifecycle: A Step-by-Step Process
At Concertium, we view risk management cybersecurity as a living, iterative process, not a one-time project. The digital world, threats, and business goals are constantly changing. The Cybersecurity Risk Management Lifecycle is a dynamic journey designed to keep you ahead of threats.
Step 1: Risk Identification & Framing
This first step is about defining the context for your risk decisions. First, we build a comprehensive asset inventory of all your digital assets: hardware, software, services, networks, and critical data. Each asset is then classified based on its importance, considering confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
Next, we tie everything back to your business objectives to align cybersecurity efforts with what truly matters. We also establish your organization’s risk tolerance—the level of risk you’re comfortable accepting—which guides resource investment. Finally, we establish the scoping of our assessment, whether it’s a specific system or the entire enterprise. This foundational step helps us understand what needs protection. Our Cybersecurity Risk Assessment Services are here to help you get that clear picture.
Step 2: Risk Assessment & Analysis
Once risks are identified, we analyze them to understand their likelihood and potential damage. We estimate the likelihood of a cyber incident using historical data, threat intelligence, and identified vulnerabilities. We then determine the potential impact, considering operational disruption, revenue loss, reputational damage, and regulatory fines.
We often use a risk matrix to combine likelihood and impact, allowing us to categorize and prioritize risks as low, medium, high, or critical. This helps focus resources on the most significant threats. We can use qualitative vs. quantitative analysis, often blending both for a comprehensive view. For vulnerabilities, we might use the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) to rate severity. Our Vulnerability Risk Management Services are designed to provide this level of clarity.
Step 3: Risk Treatment & Mitigation
Next, it’s time to choose a “treatment plan” to address the identified risks. There are four main approaches:
- Mitigate
- Transfer
- Avoid
- Accept
Mitigate is the most common strategy, involving actions to reduce a risk’s likelihood or impact. This includes implementing technical controls like firewalls, encryption, MFA, and system patching, as well as procedural controls like security policies, employee training, and robust Incident Response Plans.
To transfer risk, you shift the financial burden to a third party, such as by purchasing cyber insurance or outsourcing services. While the provider assumes some risk, ultimate accountability often remains with your organization.
To avoid risk, you discontinue the activity that creates it. For example, you might choose not to enter a new market if the cybersecurity risks are unacceptably high.
To accept a risk is a conscious decision to take no further action, typically for low-impact risks where the cost of mitigation outweighs the potential harm. Our Cybersecurity Risk Mitigation strategies help you make these informed decisions.
Step 4: Risk Monitoring & Review
The digital world is always in motion, so your risk management cybersecurity strategy must be too. This final, continuous step ensures your defenses stay effective. This stage involves continuous monitoring of your security controls, the threat landscape, and your IT ecosystem. We track threat intelligence, analyze security logs, and regularly evaluate the effectiveness of your security controls to ensure they remain robust against new threats.
Staying updated with the latest threat intelligence is crucial for anticipating dangers. As new risks emerge or regulations change, we ensure your policy updates are swiftly implemented. We even offer capabilities like Real-Time Material Breach Alerts to ensure you’re immediately aware of potential issues. This iterative lifecycle ensures your cybersecurity posture remains adaptable.
Key Frameworks and Best Practices for a Robust Strategy
A robust risk management cybersecurity strategy relies on established frameworks and best practices for a structured, governed approach. Our Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) Strategies are designed with these principles in mind.
Essential Frameworks for Risk Management Cybersecurity
Several widely recognized frameworks guide organizations in managing their cybersecurity risks:
- NIST Risk Management Framework (RMF): This flexible, seven-step process from NIST manages security and privacy risks by integrating them into the system development life cycle. It’s widely used across public and private sectors.
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF): The CSF offers a common language for managing cyber risk through five core functions: Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover. Its global adoption highlights its effectiveness in helping organizations reduce cyber risks.
- ISO/IEC 27005: This international standard provides guidelines for information security risk management, supporting the concepts in ISO/IEC 27001. It offers a structured approach to identifying, analyzing, and evaluating information security risks.
These frameworks provide a roadmap for establishing comprehensive Cybersecurity Governance Frameworks that align with your business goals.
Best Practices for an Effective Program
Beyond frameworks, certain best practices are critical for successful risk management cybersecurity:
- Executive Buy-in: Strong support from the Board and C-suite is essential for resource allocation and cultural adoption.
- Regular Assessments: Conduct frequent vulnerability scans, penetration tests, and security audits. We recommend business-level cybersecurity health checks at least bi-annually.
- Employee Training: Since the human element is often the weakest link, continuous security awareness training is paramount. It reduces human-related incidents and ensures staff understand threats and policies.
- Incident Response Cybersecurity (Concertium): Developing and regularly testing detailed incident response plans is crucial for minimizing damage and recovery time.
- Third-Party Vendor Management: With companies sharing data with hundreds of third parties, robust due diligence and continuous monitoring of vendors are vital. Our Cybersecurity Supply Chain Risk Management services help manage these risks.
Key Stakeholders and Their Responsibilities
Effective risk management cybersecurity is a shared responsibility across the entire organization.
- Board of Directors: Provides strategic oversight, sets risk appetite, ensures resources, and holds leadership accountable.
- C-Suite (CEO, CIO, CISO): The CEO champions the program, the CIO manages IT infrastructure, and the CISO leads the cybersecurity program, defines strategy, and communicates risks to leadership.
- IT and Security Teams: Implement and maintain security controls, conduct technical assessments, monitor systems, and respond to incidents.
- Legal and Compliance: Ensure adherence to regulatory requirements and advise on legal implications.
- Business Unit Leaders: Manage risks within their operations, aligning cybersecurity with business objectives. They help define what needs protection.
- All Employees: Adhere to security policies, participate in training, and practice good cyber hygiene.
This shared ownership is foundational to effective GRC: Governance, Risk, and Compliance Explained.
Overcoming Challenges and Realizing the Benefits of CRM
Implementing risk management cybersecurity has its challenges, but overcoming them brings significant benefits, turning cybersecurity from a cost into a strategic advantage. Our Risk Advisory Services in Cybersecurity are here to guide you.
Common Challenges in Implementation
Many organizations face common snags when building a strong risk management cybersecurity program.
- Resource constraints: Tight budgets, a shortage of skilled professionals, and limited time for risk management tasks are common problems.
- Evolving threats: Cybercriminals constantly develop new exploits and attack methods, making it a continuous battle to keep defenses sharp.
- Organizational resistance: Resistance to changing processes, underestimation of cyber risks, and a lack of security awareness among non-technical staff can hinder implementation.
- Technical complexity: Modern IT environments, with their mix of systems, legacy software, and numerous security tools, can make it difficult to get a clear view of risks.
- Alert fatigue: A high volume of security alerts can make it difficult for teams to spot genuine threats quickly.
Facing these challenges highlights why having the right Cybersecurity Risk Management Tools and expert guidance is so important.
The Tangible Benefits of Proactive Risk Management
Putting a strong risk management cybersecurity program in place is worth the effort. It builds a stronger, smarter, and more reliable organization.
- Financial savings: Proactive risk management helps avoid the high costs of data breaches, ransomware, and regulatory fines. It is cheaper to prevent a problem than to fix it, and it can also streamline security operations, reducing costs.
- Operational resilience: A solid program ensures business continuity during a cyber incident. Knowing your critical workflows and having defenses ready minimizes downtime and enables a quick recovery.
- Mastering risk management compliance strategies: Confidently meet legal and regulatory requirements like GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS to avoid penalties and maintain market access. Our GRC: Governance, Risk, and Compliance Explained services can help.
- Improved reputation: Demonstrating a commitment to cybersecurity builds trust with customers and partners. A strong security posture is a key differentiator.
- Informed decision-making: Leaders get clear, data-driven insights into the company’s risk profile, helping them allocate security investments for the biggest impact.
- Competitive advantage: Organizations that excel at managing cybersecurity risks stand out in the market, attracting better partners and improving their overall position.
Frequently Asked Questions about Cybersecurity Risk Management
It’s natural to have questions when diving into something as crucial as risk management cybersecurity. Let’s tackle some of the most common ones.
What is the primary goal of cybersecurity risk management?
The primary goal isn’t to eliminate all risk, which is often impossible and too expensive. Instead, risk management cybersecurity aims to identify, assess, and manage risks to an acceptable level that aligns with your business objectives and risk appetite. This involves protecting critical assets and ensuring operational resilience through smart, strategic defenses.
Is cybersecurity risk management a one-time project?
No, it is not a “set it and forget it” solution. The digital world, threats, and business objectives are constantly evolving. Therefore, risk management cybersecurity is a continuous and iterative lifecycle. It requires ongoing monitoring, assessment, and adjustment to ensure your defenses remain strong and relevant against new challenges.
Who is ultimately responsible for risk management cybersecurity in an organization?
It’s a shared responsibility. While the CISO and security team lead the efforts, ultimate accountability rests with executive leadership and the Board of Directors, who set the strategy and provide resources. However, every single employee plays a vital role by adhering to policies and practicing good cyber hygiene, making security a company-wide effort.
Conclusion
Risk management cybersecurity is essential for any modern business. It is a proactive strategy, a continuous process, and a shared responsibility involving your entire organization.
By systematically identifying, assessing, treating, and monitoring risks, you build digital resilience. This protects your assets, ensures operational continuity, and safeguards your reputation.
This journey might seem complex, but you don’t have to steer it alone. At Concertium, we bring nearly 30 years of expertise to the table. We understand that every business is unique. That’s why our innovative Collective Coverage Suite (3CS), powered by AI-improved observability and automated threat eradication, is designed to offer custom solutions that truly fit your needs. Whether you’re right here in Tampa, Florida, or anywhere else, we’re dedicated to helping you steer clear of cyber dangers.
Don’t let the ever-changing threat landscape leave your digital world vulnerable. Take the next step towards a more secure future.