AI Overview:
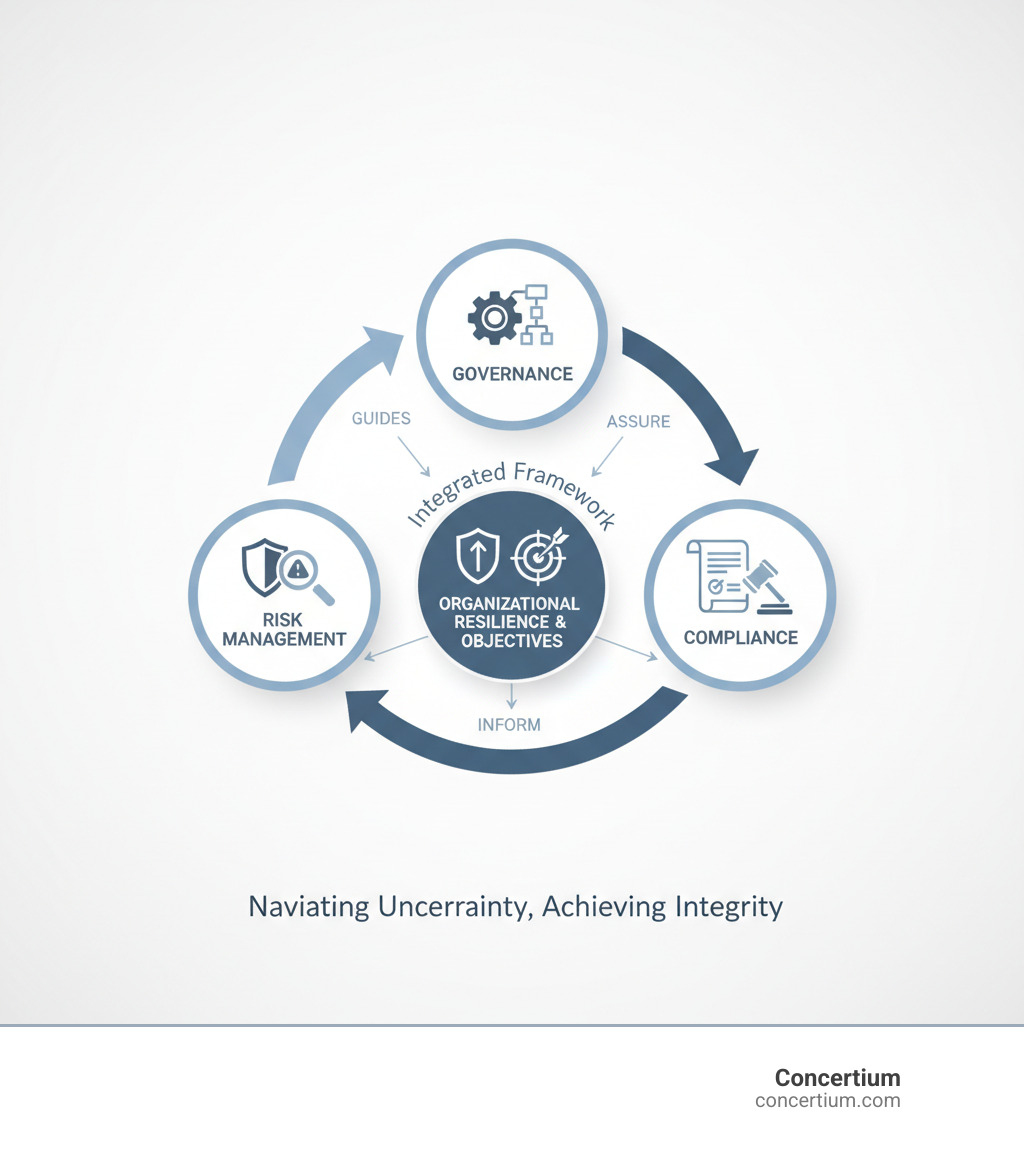
Governance and risk management (GRC) is the unified approach to achieving business goals while managing uncertainty and acting ethically. It aligns governance, risk, and compliance into a single framework—helping organizations stay agile, secure, and compliant amid growing cyber threats and regulations.
Governance and Risk: Avoid 2025’s Costly Mistakes
Why Governance and Risk Management Are Critical for Modern Businesses
Governance and risk management is no longer optional; it’s a business-critical necessity. This integrated discipline helps organizations achieve their objectives by managing uncertainty and acting with integrity. It combines three core functions:
- Governance: The structures that guide decision-making and ensure accountability.
- Risk Management: The process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating threats to business objectives.
- Compliance: The act of adhering to laws, regulations, and internal policies.
The statistics are stark. A 2023 survey found that only 53% of organizations consider their risk and compliance programs mature. Concurrently, cyber-attacks spiked in 2023, costing industries billions.
For modern businesses, this means navigating increasing regulatory requirements, sophisticated cyber threats, and complex third-party relationships. Managing these areas in separate silos is inefficient and ineffective. The solution is an integrated approach that unifies governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) into a single, coordinated framework. This eliminates redundant audits and provides a clear, unified roadmap for the organization, much like a single, reliable GPS instead of three conflicting ones.
Simple guide to governance and risk terms:
- compliance certification
- cybersecurity risk management frameworks
- enterprise compliance risk management
What is GRC? The Unified Approach to Governance, Risk, and Compliance
In many companies, governance, risk, and compliance teams work in separate bubbles, leading to duplicated efforts and a fragmented view of organizational health. GRC (Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance) solves this by creating a coordinated model that unifies these functions under a single strategy.
Formally defined in 2007 by the Open Compliance and Ethics Group (OCEG), GRC is “the integrated collection of capabilities that enable an organization to reliably achieve objectives, address uncertainty and act with integrity.” This is also known as achieving “Principled Performance®”—running a business that is both effective and ethical.
GRC dismantles the “silo mentality” where departments waste resources on overlapping audits and conflicting policies. Instead, it aligns everyone toward shared business objectives, leading to increased efficiency, reduced noncompliance risk, and better visibility across the organization.
Want to dive deeper? Check out resources like The ABCs of GRC or our guide on GRC: Governance, Risk, and Compliance Explained.
The “G”: Governance Explained
Governance is your organization’s operating system—the framework of rules and practices that dictates decision-making, accountability, and stakeholder interactions. It ensures fairness and transparency through clear ethical guidelines, defined accountability structures, and responsible resource management. Strong governance is critical for long-term success, as poor practices have been linked to major corporate failures. Key elements include stakeholder transparency, clear accountability, and robust decision-making processes. For more, explore our insights on IT Governance, Risk, and Compliance.
The “R”: Understanding Risk Management
Risk management is how your organization prepares for uncertainty. ISO 31000:2018 defines risk as “the effect of uncertainty on objectives.” This isn’t just about preventing negative outcomes; Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) also focuses on identifying “upside risks” or opportunities. The process is a continuous cycle:
- Risk identification: Spotting potential threats and opportunities.
- Risk assessment: Analyzing the likelihood and financial impact of each risk.
- Mitigation: Developing strategies to reduce or eliminate threats.
- Monitoring: Tracking risks and the effectiveness of mitigation efforts.
Effective risk management leads to better strategic decisions and more efficient resource allocation. Explore practical strategies with our resources on Cybersecurity Risk Management Tools and Compliance vs. Risk Management.
The “C”: The Role of Compliance
Compliance is your shield against legal trouble, financial penalties, and reputational damage. It ensures your organization adheres to all applicable laws, regulations, and internal policies. This includes regulatory compliance with mandates like GDPR and HIPAA, as well as industry standards.
Compliance is not a one-time task. External laws and internal policies constantly evolve, requiring continuous monitoring and adaptation. The consequences of non-compliance are severe, including fines and lost customer trust. When integrated into a GRC strategy, compliance becomes a proactive function that embeds legal and ethical conduct into your company’s culture. Learn more in our guide to the Cybersecurity Compliance Services: Top 3 Benefits.
Why a Strong GRC Strategy is Non-Negotiable
In today’s business landscape, a strong governance and risk strategy is essential. With increasingly sophisticated cyber threats and complex regulations, a single misstep can have devastating consequences.
A 2023 survey revealed that only 53% of organizations consider their risk and compliance programs mature, meaning nearly half are unprepared for critical vulnerabilities. Growth without proper risk management is a gamble. An integrated governance and risk approach provides a holistic view to spot threats early and enables data-driven decisions for safe, sustainable growth. This proactive stance builds stakeholder confidence and transforms uncertainty into a competitive advantage.
For organizations ready to move beyond reactive management, our guide on Mastering Risk Management Compliance Strategies provides the roadmap you need.
Key Benefits of an Integrated GRC Approach
Integrating governance, risk, and compliance delivers powerful benefits across your organization:
- Reduced Duplication: Streamlining audits and processes into one efficient system saves time and money, freeing up teams to focus on high-value work.
- Improved Visibility: A unified view of the organization’s risk profile allows leadership to make informed decisions and enables better resource allocation.
- Improved Business Performance: Streamlined processes and automated workflows reduce redundant tasks, driving innovation and operational efficiency.
- Stronger Stakeholder Trust: A clear commitment to ethical conduct and regulatory compliance builds confidence among customers, investors, and regulators.
- Increased Agility: A unified GRC framework allows you to respond quickly to emerging threats and changing regulations, keeping you ahead of the curve.
Learn more about this comprehensive approach in our insights on Enterprise Governance, Risk, and Compliance.
Ignoring governance and risk management can be catastrophic. The consequences of a weak GRC strategy include:
- Reputational Damage: Customer trust is hard to win and easy to lose. A single breach can cause lasting damage as negative news spreads quickly.
- Financial Penalties: Non-compliance with regulations like GDPR can result in fines reaching millions, or even 4% of annual global revenue. This is in addition to potential lawsuits and investigation costs.
- Business Disruption: A major security or compliance failure can halt operations, leading to lost revenue, plummeting productivity, and a scramble to contain the damage. Some organizations never fully recover.
In today’s threat environment, failing to invest in proper governance and risk management is not a calculated risk—it’s a gamble with your organization’s future. Protect your business with strategies from our resources on Cybersecurity Risk Mitigation and our Post-Breach Guide.
Building Your GRC Framework: From Strategy to Implementation
Building an effective governance and risk framework requires a solid blueprint. It’s a process of careful planning, using the right tools, and performing ongoing maintenance to ensure long-term stability and success.
Proven models like the GRC Capability Model from OCEG provide a practical roadmap for achieving “principled performance.” This model focuses on improving GRC maturity over time, allowing organizations to build capabilities incrementally. The journey involves critical implementation steps, from defining goals to choosing technology, and requires continuous refinement as the business and threat landscape evolve.
For a detailed guide, see our Governance, Risk, and Compliance Framework. For a cybersecurity focus, explore our Cybersecurity Governance Frameworks.
How to Effectively Implement a GRC Strategy
Successful GRC implementation requires a coordinated effort. Key steps include:
- Define Clear Goals: Establish specific objectives, such as reducing compliance violations or improving your cybersecurity posture.
- Assess Existing Procedures: Audit current processes to identify redundancies, gaps, and areas for improvement.
- Secure Executive Buy-in: Ensure senior leadership champions the initiative to drive adoption and resource allocation.
- Adopt the Right Technology: Choose GRC software that streamlines processes, provides real-time insights, and breaks down data silos.
- Train and Educate: Make sure all employees understand their roles and responsibilities within the GRC framework.
- Test and Refine: Pilot the framework on a smaller scale to work out kinks before a full-scale rollout.
For expert guidance through this process, consider our Risk Advisory Services.
Popular GRC Frameworks and Why They Are Used
You don’t need to start from scratch. Several proven frameworks can guide your GRC program:
- COSO: A framework focused on internal controls, fraud prevention, and financial reporting, often used for Sarbanes-Oxley compliance.
- ISO 31000: A flexible and broad risk management framework that can be adapted to any organization and emphasizes integrating risk management into all operations.
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework: A popular framework for managing cybersecurity risk, structured around five core functions: Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover.
- OCEG GRC Capability Model: A comprehensive model designed to break down silos and unify GRC efforts to achieve “Principled Performance®.” You can find it in the OCEG GRC Capability Model Red Book.
Many organizations blend elements from multiple frameworks to create a customized approach. See how frameworks can drive success in our analysis of Venture Capital Success with the COBIT Framework.
Common Challenges in GRC Implementation
Implementing a GRC program comes with common problems. Being aware of them is the first step to overcoming them:
- Change Management: Overcoming resistance to new processes by clearly communicating the benefits.
- Data Silos: Integrating scattered information to get a complete picture of organizational risk.
- Lack of a Comprehensive Framework: Avoiding fragmented efforts by establishing clear, overarching guidelines.
- Building an Ethical Culture: Embedding integrity into the organization’s DNA through consistent leadership and reinforcement.
- Poor Communication: Ensuring clear and consistent messaging about policies, roles, and the importance of GRC.
- Complex Regulatory Environment: Keeping pace with constantly changing laws and regulations.
Navigating these complexities is a marathon, not a sprint. Our Compliance Risk Analysis guide offers practical solutions.
The People and Technology Behind Effective Governance and Risk Management
An effective governance and risk program relies on the synergy between skilled professionals and powerful technology. This combination of human expertise and digital efficiency creates a responsive GRC ecosystem capable of protecting and advancing the organization.
Success requires cross-functional collaboration, with technology amplifying human capabilities. Tools provide automation and real-time monitoring, while human judgment provides context and strategic direction. This partnership enables organizations to achieve objectives, manage uncertainty, and act with integrity.
Explore the tools that power this synergy in our guides to Governance, Risk, and Compliance Tools and Risk and Compliance Tools.
Typical Roles and Responsibilities in a GRC Team
A strong GRC team includes several key roles:
- Chief Risk Officer (CRO): Oversees the enterprise-wide risk management strategy, reporting to the board or a risk committee.
- Chief Compliance Officer (CCO): Manages adherence to external laws, regulations, and internal policies, developing and monitoring compliance programs.
- Internal Auditor: Provides independent, unbiased assessments of GRC controls and processes to ensure they are working as intended.
- IT GRC Manager: Bridges the gap between technology and compliance, focusing on IT risk, cybersecurity, and data governance.
- Business Unit Leaders: Act as the first line of defense, responsible for implementing GRC policies in their day-to-day operations.
Understanding these roles is crucial for a cohesive team. For more on leadership distinctions, see our article on CIO vs. CISO.
The Role of Technology and GRC Tools
Technology is the backbone of modern governance and risk management. Key tools include:
- GRC Software Platforms: Centralize GRC data, automate workflows, manage policies, and streamline reporting.
- SIEM (Security Information and Event Management): Continuously monitor and analyze security data from across the IT infrastructure to detect threats in real time.
- Auditing Tools: Automate the collection and analysis of audit evidence, simplifying the evaluation of GRC activities.
- User Management and Access Controls: Ensure that only authorized personnel can access sensitive information, a fundamental aspect of security and compliance.
- AI-Powered Analytics: Revolutionize GRC by automating the analysis of regulatory changes and mapping them to existing controls. While AI offers huge benefits, it must be managed thoughtfully to address risks related to bias, privacy, and security.
Learn how these tools can transform your GRC approach on our Compliance and Risk Management Software page and find the benefits of Managed Detection and Response.
Frequently Asked Questions about Governance and Risk
What is the main goal of governance and risk management?
The primary goal of governance and risk management is to enable an organization to reliably achieve its objectives, address uncertainty, and act with integrity. It aligns the company's strategic vision with its day-to-day operations by managing risks (from financial uncertainties to cyber attacks) and ensuring compliance. It builds a resilient organization that can turn challenges into a competitive advantage.
How does GRC help with cybersecurity?
GRC integrates cybersecurity into the overall business strategy, moving it from a siloed IT function to a shared responsibility. It provides a structured framework to:
Identify and assess cybersecurity risks across all systems and processes.
Implement appropriate controls and security measures to mitigate those risks.
Ensure compliance with data protection regulations like GDPR and HIPAA.
Align cybersecurity efforts with business objectives, building customer trust.
This shifts the organization from a reactive to a proactive security posture. Our Cybersecurity Risk Assessment Services can help build this integrated approach.
How do you measure the success of a GRC program?
Success is measured using both quantitative and qualitative indicators. Key metrics include: A reduction in compliance violations and fines.
Lower audit costs and faster audit cycles.
Improved risk identification and faster response times.
Higher scores on GRC maturity assessments.
Improved stakeholder confidence and a stronger organizational reputation. A 2023 survey found only 53% of programs are considered mature, showing significant room for improvement and the need for clear metrics to track progress.
Conclusion: Achieving Principled Performance
In today’s business landscape, governance and risk management is no longer a background function—it’s the foundation of organizational resilience and success. Integrating governance, risk, and compliance eliminates inefficient silos and fosters transparency, accountability, and operational excellence.
With only 53% of organizations reporting mature risk programs and cyber-attacks on the rise, a proactive GRC strategy is essential for protection and competitive advantage. This commitment to “Principled Performance®” turns risk and compliance from cost centers into strategic enablers for sustainable growth.
The path to GRC maturity is an ongoing journey that requires the right people, advanced technology, and a culture of integrity. The organizations that invest in this journey today will be the leaders of tomorrow.
The regulatory and threat landscape is complex, but you don’t have to steer it alone. With nearly 30 years of cybersecurity expertise and our unique Collective Coverage Suite (3CS), Concertium is here to help.
Ready to transform uncertainty into opportunity? Strengthen your organization’s resilience with expert IT Governance, Risk, and Compliance services and build the principled performance that will carry your business confidently into the future.